Current Assets Definition
Current assets are assets which are held by a business for a short period, mainly a year, or within an accounting cycle of a business. These are balance sheet accounts which can either be converted to cash or used to pay current liabilities within the same time frame.
These are typically seen as those assets which can easily be converted to cash to pay off current liabilities and outstanding debt payments.
Greater the number higher the liquidity of a company which leads to more working capital. It is important because it is used day in and day out to pay off a firm’s usual expenditure which is important for its operations. Such expenses include utility bills, short-term debts, overheads etc.
Examples of Current Assets
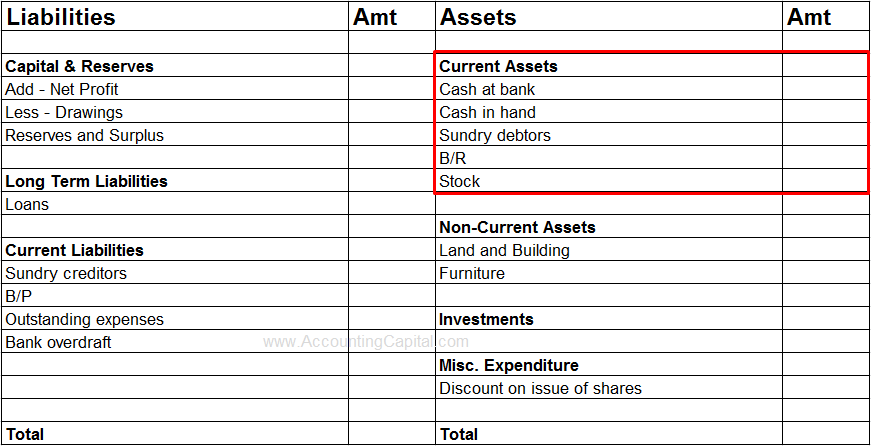
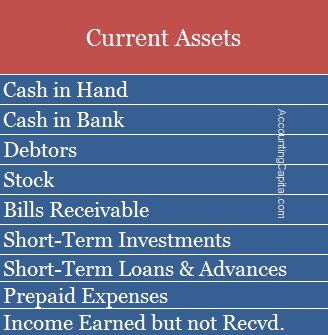
The list of current assets includes Cash, Bank, Debtors, Stock, Prepaid Expenses, etc. They are shown on the Assets side of the balance sheet.
Such short-term assets are also called circulating assets, circulating capital, or floating assets.
Related Topic – What are Intangible Assets?
Placement in Financial Statements & Ratios
They are shown in the assets section of the balance sheet.
The current ratio which can be calculated as CA/CL also highlights the importance of having enough short-term assets vs. short-term liabilities.
It is used to determine the current assets turnover ratio for a company enabling evaluation of how well the company is using them to generate revenue. It can be calculated as (Total Net Sales/Average Current Assets).
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
Revision & Highlights Short Video
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 20 – Current Assets
>Read Format of Balance Sheet