Liquid Assets
The term is usually encountered when dealing with assets which are highly liquid in nature. Liquid assets are either cash, cash equivalents or they can be converted into cash at very short notice. They are also referred to as Quick Assets.
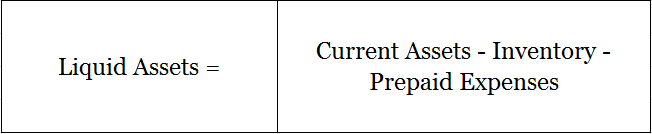
Quick assets can be calculated as [Current Assets – Inventory – Prepaid Expenses]. Inventory and prepaid expenses cannot be converted to cash within a very short period of time.
Examples of liquid assets are;
- Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Short-Term Loans and Advances
- Bills Receivable
- Debtor – Provision for Doubtful Debts
- Short-term Investments
Uses and Applications of Liquid Assets
Such resources are used to identify the liquidity of a company with the help of Liquid Ratio/Quick Ratio. This ratio helps to compare a firm’s liquid assets with its current liabilities and assess its short-term solvency.
They are considered a more accurate indicator of the company’s short-term debt paying capability as compared to the current ratio. In other words, the ratio is very important for banks and other financial institutions to understand the actual liquidity of the company.
A comparison between the current ratio and liquid ratio may reveal the extent of stock held up in the business.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 27 – Liquid Assets
>Read Accounting Ratios
