Reserves in Accounting
At the end of a financial year when a company earns a profit certain portion of it is retained in the business to meet future contingencies, growth prospects, etc. This amount of money kept aside is termed as reserves. Reserves are a component of retained earnings.
They help in fortifying the financial position of a company and can be used for various purposes such as expansion, stable dividend repayments, legal requirements, meeting contingencies, improving the financial situation, investments, etc.
Examples – General reserve, Reserve for Dividends Equalization, Reserve for Expansion, Reserve for Increased Cost of Replacement etc.
There are mainly 2 different types of reserves; Capital and Revenue.
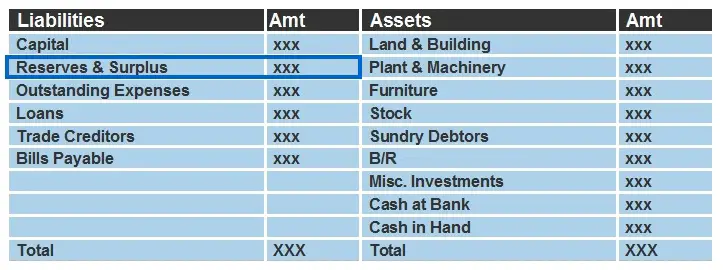
Inside Financial Statements
Reserves are shown on the liability side of a balance sheet under the head “Reserves and Surplus” along with capital. If a company faces losses then it may not be created, at all.
Provisions are different, they are mandatory and created as guided by the accounting principles whereas reserves are a choice.
 Related Topic – What is a Contra Liability?
Related Topic – What is a Contra Liability?
Types of Reserves – Capital Reserve
They are created out of capital profits & are usually not distributed as dividends to shareholders. It cannot be created out of profits earned from the core operations of a company.
Examples
- Profit earned before a company’s incorporation
- Premium earned on the issue of shares & debentures
- Profit on re-issuance of forfeited shares
- Profit set aside for redemption of preference shares or debentures
- Profit on sale of fixed assets
- The surplus on revaluation of assets and liabilities
- Capital redemption reserve
Types of Reserves – Revenue Reserve
They are created out of profits earned from the operations of a company. It is reflected in profit and loss appropriation account. It can be used for the following:
- Dividend to shareholders
- Expansion of business
- Stabilize the dividend rate
They are divided into two types & both of them are kept aside as appropriation for profits.
- General Reserves – As the name suggests, they are created out of profits & kept aside for the general purpose and financial strengthening of the company, it doesn’t have any special purpose to fulfil and can be used for any viable reason in future. Top reasons include meeting contingencies and expansions that can’t be foreseen.
- Specific Reserves – This reserve, however, is created keeping a specific reason in mind and can only be used for its designated purpose. Examples include Dividend Equalization Reserve, Debenture Redemption Reserve, Contingency Reserve, Capital Redemption Reserve etc.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Read Difference Between Reserves and Provisions
