Bookkeeping
Bookkeeping is the process of recording all financial transactions of a business unit in a systematic way on a day-to-day basis. Most common examples of records are:
- Receipts from customers
- Payments to suppliers
- Billing for products supplied
- Recording invoices from suppliers
- Recording depreciation and other adjustments etc.
Bookkeeping acts as a basis for the accounting process. A bookkeepers’ duty is to record each transaction in the corresponding day-book or journals. A competent bookkeeper records the financial transactions such a way that it gives a clear picture of activities performed inside a business unit.
The last stage of bookkeeping is to prepare the trial balance, find and correct errors. Based on this, an accountant prepares the financial statement of the company.
Example of Bookkeeping
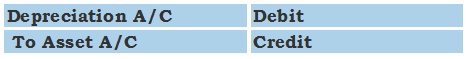
Part of bookkeeping involves entering a transaction into a journal and then getting it posted to a ledger account. This first step shows a transaction of depreciation being recorded in a journal book in the form of a journal entry.
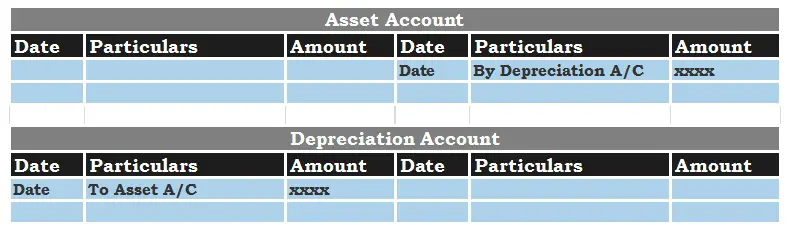
Once the above journal entry is posted in their respective ledger accounts it will show up as below.
Purpose of Bookkeeping
A business unit is involved in various financial transaction every day and over time it becomes difficult to keep track with these millions of transactions and use them for future reference.
Bookkeeping helps in organizing the data logically and chronologically for its further usability. Besides, bookkeeping is done also to:
- Understand the financial effect of each transaction
- Determine the factors responsible for profit or loss in a certain period
- Avoid errors in the process of accounting
- Determine tax-liability
Types of Bookkeeping
There are mainly two methods of bookkeeping – single entry method and the double-entry method. Sometimes a combination of both methods is also used.
The single entry system is most suitable for small businesses. Here only payments, receipts, sales and purchases are recorded. Inventory, capital and others such entries are recorded as notes. However, the system is not free from error and to some extent incomplete. Double-entry bookkeeping system, contrast, is detailed and complex.
Here using the idea of debit and credit, every transaction is recorded twice: what is received (debit) and what is given up (credit). This is the standard method of bookkeeping used by bookkeepers and accountants.
Consider the example of Unreal Pvt. Ltd purchasing a car for business purposes and paying 2,00,000 for this. In a single entry system, only the purchase activity and amount will be recorded whereas in double entry system the amount will be recorded twice, debited as car purchase and credited on account of cash.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Read Difference between Bookkeeping and Accounting