Tangible Assets Vs Intangible Assets
An asset is a useful/valuable thing or person. Assets are divided in various ways depending on their physical existence, life expectancy, nature, etc. The difference between tangible assets and intangible assets is purely based on their physical existence in a business.
In simpler words, an asset is a piece of property owned by an individual or organization which is recognized as having value and is available to meet obligations.
Tangible Assets
The best way to remember tangible assets is to remember the meaning of the word “Tangible” which means something that can be felt with the sense of touch. Assets which have a physical existence and can be touched and felt are called Tangible Assets. The main difference between tangible and intangible assets is where one can be touched and felt the other only exists on paper.
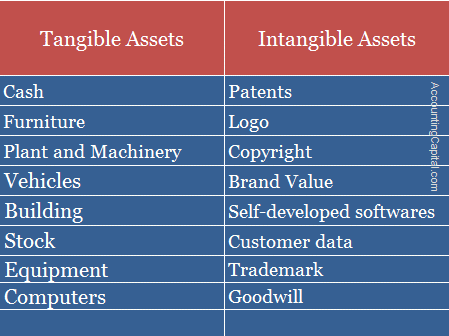
Tangible assets can include both fixed and current assets. A few examples of such assets include furniture, stock, computers, buildings, machines, etc.
Intangible Assets
The opposite of tangible assets, Intangible assets don’t have a physical existence and cannot be touched or felt. Intangible assets can either be definite or indefinite, depending on the kind of asset in question.
A few examples of such assets include goodwill, patent, copyright, trademark, company’s brand name, etc.
A patent is a definite intangible asset as it will expire after the patent is over, however, a company’s brand name will remain over the course of the company’s existence.
Related Topic – Difference between Current Assets and Current Liabilities
Difference between Tangible and Intangible Assets (table format)
| Tangible Assets | Intangible Asset |
|---|---|
| 1. They have a physical existence. | 1. They don’t have a physical existence. |
| 2. Tangible assets are depreciated | 2. Intangible assets are amortized. |
| 3. Are generally much easier to liquidate due to their physical presence. | 3. Are not that easy to liquidate and sell in the market. |
| 4. The cost can be easily determined or evaluated. | 4. The cost is much harder to determine for Intangible assets. |
| 5. They have a scrap value. | 5. They do not have a scrap value. |
| 6. May be accepted by financial institutions as collateral. | 6. They are not accepted by financial institutions as collateral. |
| 7. Such assets are held both on paper and by possession. | 7. Such assets are held just on paper. |
| 8. Examples: Vehicles, Plant & Machinery, etc. | 8. Examples: Software, Logo, Patents, etc. |
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
Revision & Highlights Short Video
Highly Recommended!!
Do not miss our 1-minute revision video. This will help you quickly revise and memorize the topic forever. Try it :)
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 26 – Intangible Assets
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 32 – Tangible Assets
>Read What are Contingent Assets?
