Deferred Revenue Expenditure
It will be easier to understand the meaning of deferred revenue expenditure if you know the word deferred, which means “Holding something back for a later time”, or “postpone”.
Deferred Revenue Expenditure is an expenditure that is revenue in nature and incurred during an accounting period, however, related benefits are to be derived in multiple future accounting periods.
These expenses are unusually large in amount and, essentially, the benefits are not consumed within the same accounting period.
Part of the amount which is charged to the profit and loss account in the current accounting period is reduced from total expenditure and the rest is shown in the balance sheet as an asset (fictitious asset, i.e. it is not really an asset).
Related Topic – What is Capital Expenditure and Operational Expenditure?
Example
Suppose that a company is introducing a new product to the market and decides to spend a large amount on its advertising in the current accounting period. This marketing spend is supposed to draw benefits beyond the current accounting period.
It is a better idea not to charge the entire amount in the current year’s P&L Account and amortize it over multiple periods.
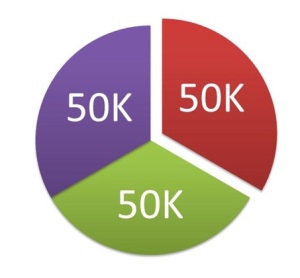
The image shows a company spending 150K on advertising, which is unusually large as compared to the size of their business.
The company decides to divide the expense over 3 yearly payments of 50K each as the benefits from the spending are expected to be derived for 3 years.
*Large losses originating from unforeseen circumstances, such as a natural disaster or fire, etc., may also be treated as deferred revenue expenditure.
Reasons
- The benefits of such an expense are to be received in the future financial years. Therefore, it is logically incorrect to record 100% of such expenses as revenue expenditures and write them off in the current accounting period.
- In most cases, these expenses are so large that they may consume all the profits of the company if written off in the current accounting year. As a result, the users of accounting information will get a false impression.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
Revision & Highlights Short Video
Highly Recommended!!
Do not miss our 1-minute revision video. This will help you quickly revise and memorize the topic forever. Try it :)
>Read Fictitious Assets
