Table of Contents
Introduction
A bank is a financial institution that helps individuals and businesses with fund requirements & financial transactions. A bank overdraft is when account holder(s) withdraw more money from their bank account than they have. It creates a credit balance in the account.
Overdrafts usually come with interest. It’s like a fee for borrowing money. When a business pays back the overdraft amount, it is done with an interest. Overdrafts are convenient to use when short-term funds are needed immediately.
It can be used by a business for various reasons such as;
- When a company is having short-term issues with cash.
- For day-to-day operations, because there isn’t enough working capital.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Payment to Creditor
Journal Entry
As per the modern rules, the journal entry for bank overdrafts will be;
| Bank A/c | Debit |
| To Bank Overdraft A/c | Credit |
(Being overdraft account used and bank account credited with funds)
“Bank account” is debited since money is being brought into the firm. This leads to an increase in money (assets).
“Bank overdraft” account is credited as it is to be paid back to the bank in the short term. It is a current liability for the business.
As per the traditional rules, the journal entry for bank overdrafts follows the below rules;
- Bank A/c – It follows the rule of a personal account which is “debit the receiver, & credit the giver”. As the company’s bank account is receiving money the bank account will be debited.
- Bank OD A/c – It is a personal account as well which follows the same rules. As the bank is lending money to the company, it is “the giver”. Hence, the Bank Overdraft account will be credited as per the personal account rule.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Cheque Received from Debtor
Example of the Accounting Entry for Bank Overdrafts
The firm Blue Stars used an overdraft for 20,000 from their HSBC bank account.
The journal entry for bank overdrafts in the book the Blue Stars;
| HSBC Bank A/c | 20,000 |
| To Bank Overdraft A/c | 20,000 |
(HSBC overdraft used & account credited with 20,000)
Blue Stars is borrowing funds from the bank therefore there is an increase in the assets. This is debited. As a result, 20,000 is debited in the HSBC Bank A/c.
The bank is lending money which leads to an increase in liabilities. This is credited. As a result, the Bank Overdraft A/c will be credited with 20,000.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Bank Charges Paid
Impact on the Financial Statements
This accounting entry has an impact on the Balance sheet. There will be an increase in the liabilities under current liabilities. This is because the business is borrowing funds from the bank and it needs to be repaid with a possible interest component.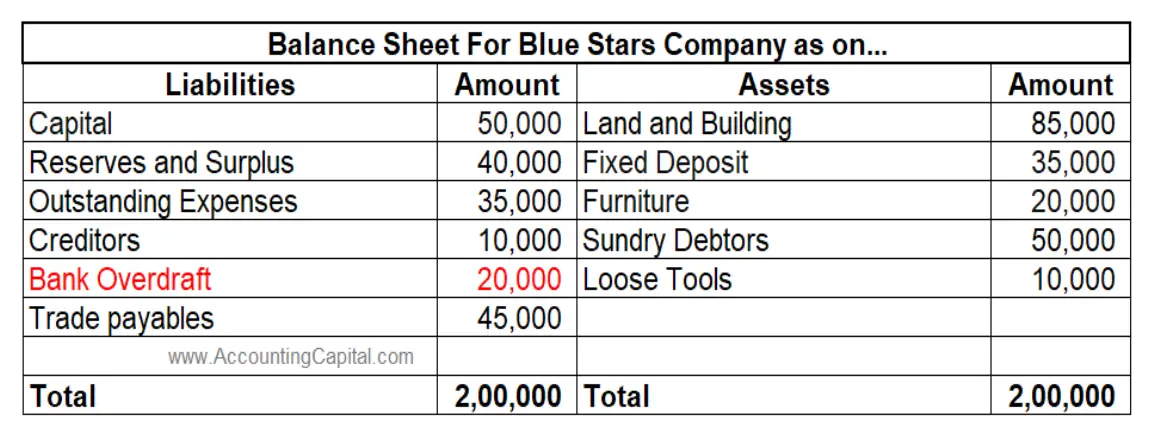 The above example shows an increase in the liabilities (current) as a “bank overdraft”.
The above example shows an increase in the liabilities (current) as a “bank overdraft”.
This journal entry will not have an impact on the Income statement. It will appear in the income statement as an additional expense when the company pays interest to the bank.
This journal entry will also have an impact on the Cash flow statement. The repayment of the overdraft will be seen as cash outflow under financing activities.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Payment to Vendor
Conclusion
To deal with the overdrawn account, this journal entry is made in accordance with the month-end checklist.
- Account holders can use an overdraft to handle unforeseen expenses or low liquidity situations without facing immediate financial strains.
- By adhering to the chart of accounts and performing regular reconciliations, a firm ensures that its financial statements accurately represent the company’s financial health.
- Overdrafts come with high interest rates, so users need to be aware. It’s important to stay on top of the interest rate since they can change.
- If used wisely an overdraft from the bank can be a great resource. It can be used to bridge short-term financial gaps.
- This ensures that the company’s financial statements are accurate and in line with the reconciled bank statement.
This journal entry will impact financial ratios like current ratio, quick ratio, interest coverage ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, etc.
>Read Journal Entry for Investment in Subsidiary
