There are expenses that are due but have not been paid as of the end of the current accounting period. Such expenses are called outstanding expenses. The benefits of such expenses have been consumed although due to some reason they are not paid. We’ll explain how to pass a journal entry for outstanding expenses in this article.
Outstanding expense is a “personal” account as per the traditional classification of accounts and a “liability” as per the more recent way of accounting.
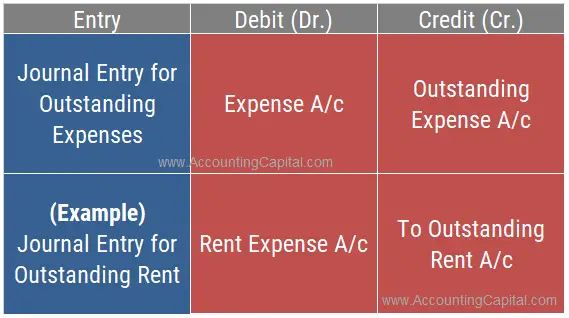
Journal Entry for Outstanding Expenses
| Expense A/C | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Expense A/C | Credit | Credit the increase in liability |
The outstanding expenses journal entry involves two accounts: the “Outstanding Expense Account” and the related “Expense Account”.
They are an obligation for the business and therefore treated as a liability. The accounting rule applied is “credit the increase in liability” and “debit the increase in expense” (modern rules of accounting).
They are also known as expenses due but not paid and should be shown in the financial books to avoid overstatement of earnings.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Outstanding Subscription
Simplifying Outstanding Expenses Entry with an Example
Question – On December 31st 20YY Company-A recognised rent due for 100,000 related to the same year. The period has ended and the payment has not been made.
The same is paid in cash next year on January 10th. Show all financial recordings including the journal entry for outstanding expenses on these dates;
- December 31st 20YY (Same day)
- January 10th (Next year, when it is actually paid)
1. December 31st 20YY – (Overdue expense recorded as outstanding)
| Rent Expense A/c | 100,000 |
| To Outstanding Rent A/c | 100,000 |
2. January 10th – (Payment made towards outstanding rent in next year)
| Outstanding Rent A/c | 100,000 |
| To Cash A/c | 100,000 |
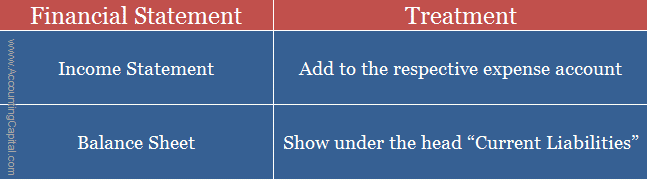
Treatment of Oustanding Expenses in Financial Statements
Once the journal entry for outstanding expenses has been posted they are then placed appropriately in the final accounts.
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Prepaid Expenses
Journal Entry for Outstanding Rent
A rent which is past its due date is called outstanding rent. Such an obligation is included in the list of current liabilities for a business and the account is treated as a representative personal account.
Let’s assume that in the month of March there was 30,000 past due as a rent amount that wasn’t paid for some reason.
When rent is overdue, here is the outstanding rent journal entry that is recorded,
| Rent Expense A/c | Debit | Dr. the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Rent A/c | Credit | Cr. the increase in rent liability |
(Being unpaid rent recorded)
Related Topic – How to Show Outstanding Expenses in Trial Balance?
Journal Entry for Outstanding Salary or Wages
Salaries and wages differ slightly. Part-time jobs, assignments with variable hours, and jobs with repetitive duties are commonly referred to as wages instead of salaries.
Wages are generally paid on a weekly, biweekly, or monthly basis. Generally, the difference between salary and wage is that salary is a fixed amount and wage is based on the number of hours that an employee works.
Pass outstanding salary journal entry in the books of Unreal Corp. using the below trial balance and supplementary information provided along with it.
- Outstanding Salaries – 30,000
- Outstanding Wages – 20,000
Extract from Trial Balance of Unreal Corp.
| Account | Dr. | Cr. |
| Salaries | 70,000 | |
| Wages | 80,000 |
Outstanding Salaries Journal Entry in the Books of Unreal Corp.
| Salary A/c | 30,000 |
| To Outstanding Salary A/c | 30,000 |
(Salaries due in the previous year are transferred to “Outstanding Salary A/c”)
Journal Entry for Outstanding Wages in the Books of Unreal Corp.
| Wages A/c | 20,000 |
| To Outstanding Wages A/c | 20,000 |
(Wages related to the previous year transferred to outstanding wages account)
Related Topic – Example of a Service Center
Journal Entry for Outstanding Interest
It is also known as accrued interest. An outstanding interest journal entry is required to record the amount of interest owed by the business on a loan obligation. It refers only to the portion of the interest that is currently due but not paid by the borrower. It is a “receivable” for the lender.
Suppose in the month of December, interest on a bank loan taken from ABC bank was due at 24,000. Pass the accounting entry for outstanding interest at the end of the year i.e. 31st Dec.
| Interest Expense A/c | 24,000 |
| To Outstanding Interest A/c | 24,000 |
(Recording interest overdue at 24,000)
Related Topic – Difficult Adjustments in Final Accounts
Are Outstanding Expenses Debited or Credited?
Outstanding expenses are obligations yet to be paid by the firm. They are “credited” as per two rules of accounting,
- Personal A/c – Cr. the giver
- Treated as a Liability – Cr. the increase in liability
Such past due expense is debited to Profit & Loss A/c because it is prepared as per the accrual basis of accounting which says that “irrespective of when the payment is made, all expenses and incomes should be recorded in the period when they occurred.
An outstanding expense is one that has been incurred but has not yet been paid. Despite the fact that it has not been paid, it belongs to the same accounting period. Therefore, it is added to the debit side of a profit & loss account.
Related Topic – Is an Expense Debit or Credit?
Are such Outstanding Expenses Debts?
Debt is typically in the form of money, that is due or owed. However, in day-to-day accounting vocabulary, a “debt” may be referred to as long-term debt i.e. an obligation that is payable beyond 12 months.
Outstanding expenses are a liability for the firm but they are not considered a debt for the company. Due to the fact that outstanding expenses are expected to be paid within 12 months, they are treated as current liabilities.
Related Topic – Are Bad Debts Liabilities?
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 34 – Outstanding Expenses
>Read Top Accounting and Finance Interview Questions

