Amortization
Reduction in the value of an intangible asset by prorating its cost over a period of time (generally in multiple accounting periods) is called Amortization. Point worth remembering is that it can only be done for intangible assets such as copyrights, patents, trademarks, goodwill, etc. It is used for writing-off intangible assets whereas depreciation is used for tangible assets.
If related to obligations, it can also mean payment of any debt in regular instalments over a period of time. Home and other loans often talk about such amortization schedules.
If an intangible asset has an unlimited life then a yearly impairment test is done, which may result in a reduction of its book value.
Related Topic – Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
Example
Suppose a company Unreal Pvt Ltd. develops new software, gets copyright for 10,000, and it is expected to last for 5 years.
Now, if the company shows the entire 10,000 as an expense, it will not show the true and fair picture for that accounting period and the profits for that year will show deflated numbers. Hence, every year the company shall record 2,000 for 5 years to write off the copyright’s entire cost, 2,000 X 5 Years
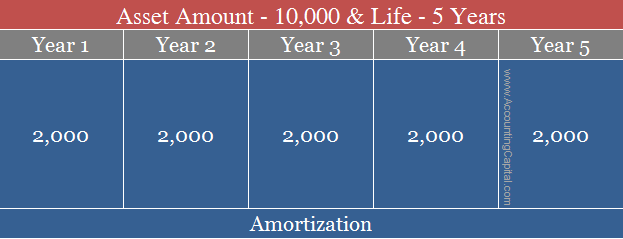
This will be seen as amortization of the copyright with the straight-line method. Writing off the entire copyright’s amount in 5 years over 5 equal instalments.
Accounting & Journal Entry for Amortization
Assuming that no contra account was prepared and the reduction was done directly from the intangible asset, the journal entry would be as follows;
| Amortization Expense A/C | Debit |
| To Intangible Asset A/C | Credit |
Only to the extent related to the current financial year, the remaining amount is shown in the balance sheet as an asset.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 15 – Amortization
>Read Intangible Assets Vs Tangible Assets
