Overview of Interest received from Bank
When a business has excess funds, it invests these funds by depositing them in the bank rather than keeping the money idle because banks provide interest on the money deposited. When the business deposits its funds in the bank they receive interest as a percentage of the amount deposited.
The interest earned by the business from the bank is an indirect income and is credited to the Profit and Loss account or Income Statement. According to the accrual concept of accounting, the accrued interest is added to the Interest received from bank A/c and recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet.
Journal entry as per Modern Rules of Accounting
| Account | Increase | Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Income | Credit (Cr.) | Debit (Dr.) |
| Asset | Debit (Dr.) | Credit (Cr.) |
Interest is an income for the organization and the interest received from the bank is an increase in income. Thus, it is credited to the financial books according to the modern rules of accounting.
The bank balance is a current asset. When the interest income is received, it increases the bank balance thus, an increase in assets is debited according to the modern rules of accounting.
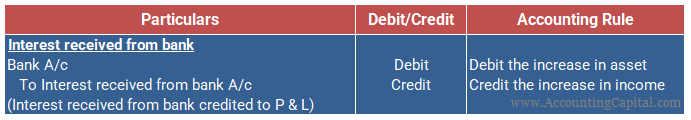
The journal entry for recording interest received from the bank is provided below: (Rule Applied: Debit the increase in Asset and Credit the increase in Income)
Example
Ms. Jane invested 50,000 in fixed deposits at her bank for 1 year. If the prevailing interest rate for fixed deposits is 7% per annum, Ms. Jane received 3,500 as interest at the end of the year. Therefore, ‘Interest Received A/c’ is credited (income) and ‘Bank A/c’ is debited (receiver). The journal entry for the same is given below.
Journal of Mr. Alex
| Bank A/c | 3,500 | Debit |
| To Interest received from a bank A/c | 3,500 | Credit |
(Being interest @ 7% p.a received from the bank at the end of the year.)
Journal entry as per Golden Rules of Accounting
| Account | Rule for Debit | Rule for Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal | Debit all expenses and losses | Credit all incomes and gains |
| Personal | Debit the Receiver | Credit the Giver |
Interest received from a bank is classified as a “nominal account”. A nominal account represents any accounting event that involves expenses, losses, revenues, or gains. It is what you would call a profit and loss or an income statement account. As per the golden rule of accounting for a nominal account, interest received from the bank is an income and is credited to the books of accounts.
A bank Account is classified as a “personal account” and as per the golden rule of accounting for personal accounts “we debit the receiver and credit the giver.” Hence, we debit the bank account.
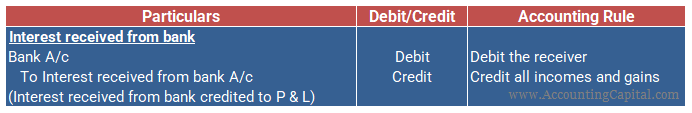
The journal entry for recording interest received from the bank is provided below: (Rule Applied: Debit the Receiver and Credit all incomes and gains)
Example
Mr. Alex has a savings account with ABC Bank. The passbook showed a balance of 100,000 at the end of the month. The bank offers interest at the rate of 6% per annum on such a balance. Therefore, ‘Interest Received A/c’ is credited (income) and ‘Bank A/c’ is debited (receiver). The journal entry for the same is given below.
Journal of Mr. Alex
| Bank A/c | 500 | Debit |
| To Interest received from a bank A/c | 500 | Credit |
(Being interest @ 6% p.a received from the bank for a month.)
Interest Received from Bank in Trial Balance
Interest received from the bank shows a credit balance. A trial balance example showing a credit balance for the same is provided below.
