Overview of Liabilities
From a business perspective, a liability is defined as money owed to third parties. It may be external (3rd parties) or internal (promoters). It is a debt or financial obligation that is settled by an exchange of economic benefits at a future date. For example, long-term loans, bonds payable, trade payables, bills payable, short-term loans, bank overdraft, etc.
Classification of Liabilities
- Internal & External Liabilities – Internal liabilities include all obligations that a business has to pay back to internal parties. For e.g. promoters (owners), employees, etc.
- Current liabilities: The liabilities that are payable within one year. For Example- Creditors, bank overdraft
- Non-current liabilities: The liabilities that are payable after a period of more than one year. For Example- long-term loans, debentures
- Contingent liabilities: The liabilities that are payable depending on the occurrence of a particular event. For Example- lawsuit proceedings, guarantee for loans
In accounting terms, liabilities are the funds payable to outsiders. Thus, an increase in liability should be credited to the books of accounts.

Related topic – Where is Amortization Shown in Financial Statements?
As per the Modern Rules of Accounting
| Account | Increase | Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Liability | Credit (Cr.) | Debit (Dr.) |
Liability is Credited (Cr.) when increased & Debited (Dr.) when decreased.
Why is it like this?
This is a rule of accounting that cannot be broken under any circumstances.
How is it done?
For instance, a local business borrowed a sum from the bank for expanding its operations. As a result, this loan would be a liability and would be shown on the balance sheet for the current accounting year since the borrowed money increases the liability of the business.
Given below is the journal entry to be recorded at the time of borrowing the loan: (Rule Applied – Cr. the increase in liability)
| Bank A/c | Debit |
| To Loan from bank A/c | Credit |
(Sum borrowed from the bank for expansion)
The balance in the loan account decreases when payment is made towards amortization.
Related topic – Are Bad Debts Recorded in the Income Statement?
As per the Golden Rules of Accounting
| Account | Rule for Debit | Rule for Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Personal | Debit the Receiver | Credit the Giver |
Liability is credited as per the Golden Rules
The individuals and other organizations that have direct transactions with the business are called personal accounts. Liabilities such as creditors, outstanding expenses, income received in advance, loans taken, etc. are classified as personal accounts. Personal accounts are recorded on the balance sheet of the organization.
As per the golden rules of accounting (for personal accounts), liabilities are credited. In other words, the giver of the benefit is a liability to the one who receives it.
Example
For instance, you own a stationery shop and you purchased pens from the manufacturer on credit. You agreed to make the payment for pens after 30 days. Thus, the amount payable to the supplier is a liability to you and is credited to your books of accounts.
Given below is the example of a journal entry to be recorded at the time of credit purchase: (Rule Applied – Credit the giver )
| Purchases A/c | Debit |
| To Creditor / Supplier A/c | Credit |
(Pens purchased on credit)
Related topic – List of Liabilities in Accounting
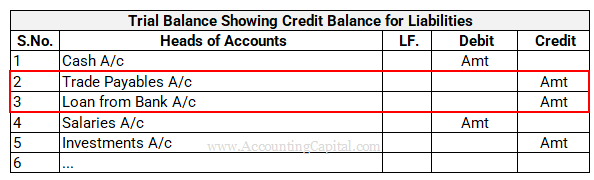
Liabilities Inside Trial Balance
Liabilities show a credit balance in the trial balance. A trial balance example showing a credit balance for reserves, trade payables, and loans is provided below.
>Read What is the Meaning of Assets have Debit Balance and Liabilities have Credit Balance?
