What are Retained Earnings?
Retained Earnings are the accumulated net income of an entity at the end of an accounting period that is retained by it to meet any future contingencies, invest in expansion activities, pay dividends to its shareholders, share buybacks, or issue bonus shares.
| Retained Earnings Calculation |
| Opening Retained Earnings |
| + or – (plus/minus) |
| Net Profit or Net Loss for the current period |
| – |
| Dividend Paid in the Current Period |
| + or – |
| Prior Period Adjustments |
Retained Earnings are a part of “Shareholders Equity” presented on the “Liabilities side” of the balance sheet as it indicates the company’s liability to the owners or shareholders.
The company cannot utilize the retained earnings until its shareholders approve it. Thus, retained earnings are credited to the books of accounts when increased and debited when decreased. If the balance of retained earnings is negative, then it is referred to as accumulated losses/deficit, or retained losses.
As per the Modern Rules of Accounting
| Account | Increase | Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Liability | Credit (Cr.) | Debit (Dr.) |
Retained Earnings (liability) are Credited (Cr.) when increased & Debited (Dr.) when decreased.
Why is it like this?
According to this rule, an increase in retained earnings is credited and a decrease in retained earnings is debited. This is a rule of accounting that cannot be broken under any circumstances.
How is it done?
1. Retained Earnings are credited with the Net Profit earned during the current period. Crediting the retained earnings will increase its balance.
Example
Samsung Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company decided to retain the profits for that year and invest the retained earnings in expanding the business. This increase in retained earnings is credited to Retained Earnings Account.
Given below is the journal entry to be recorded: (Rule Applied – Cr. the increase in liability)
| Net Profit A/c | 500,000 | Debit |
| To Retained Earnings A/c | 500,000 | Credit |
(Transferring net profit earned to retained earnings.)
2. Some instances which reduce the balance of retained earnings are-
a. Net loss during the current period
b. Dividend payable
c. Bonus Shares issued, etc.
Retained Earnings will be debited with these transactions.
Example
Shareholders of Apple Inc. approve the dividend declared by the board of directors amounting to 100,000. The dividend payable reduces the balance of retained earnings so it is debited in the financial books.
Given below is the journal entry to be recorded: (Rule Applied – Dr. the decrease in liability)
| Retained Earnings A/c | 100,000 | Debit |
| To Dividend Payable A/c | 100,000 | Credit |
(Dividend to be paid from retained earnings.)
As per the Golden Rules of Accounting
| Account | Rule for Debit | Rule for Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Personal | Debit the Receiver | Credit the Giver |
Retained Earnings (Liability) are credited as per the Golden Rules
Since retained earnings are a part of shareholders’ equity, it is an obligation of the company to pay it back to the owners. Thus, it is a liability of the company and it is credited as per the golden rules of accounting for personal accounts.
Example
HP Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company decided to retain the earnings for that year and utilize them for further growth. This is a liability (shareholders’ fund) of the company to pay the earnings back to the shareholders. Thus, the retained earnings are credited to the Retained Earnings Account.
Given below is the journal entry to be recorded: (Rule Applied – Cr. the giver)
| Net Profit A/c | 500,000 | Debit |
| To Retained Earnings A/c | 500,000 | Credit |
(Transferring net profit earned to retained earnings.)
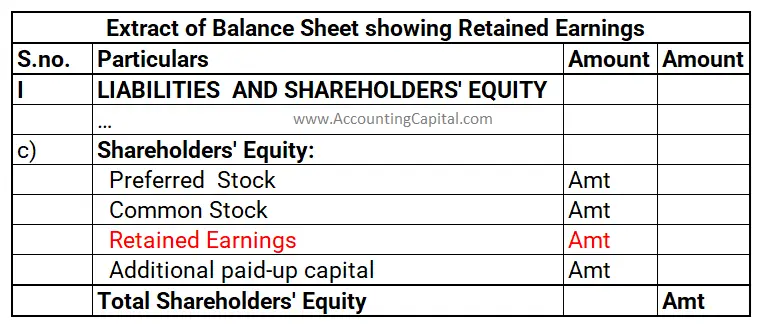
Retained Earnings inside the Balance Sheet
Retained earnings show a credit balance and are recorded on the balance sheet of the company. A balance sheet example showing retained earnings is provided below.
Conclusion
The key takeaways from the above discussion are:
- Retained earnings are the incomes retained by a business for future contingencies, reinvestment, expansion, or any other purpose.
- Retained Earnings are a part of “Shareholders Equity” presented on the “Liabilities side” of the balance sheet.
- If the balance of retained earnings is negative, then it is referred to as accumulated losses/deficit, or retained losses.
