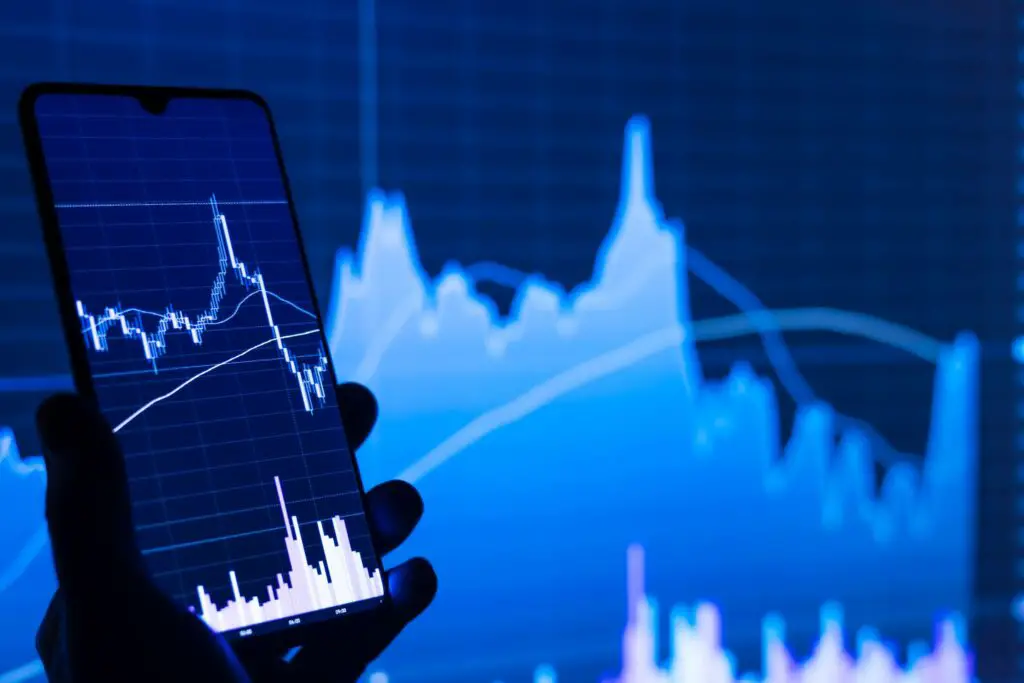
Getting into the stock market is exciting. There are plenty of stock options to choose from, and there’s always something happening that keeps you hooked on continuing to trade. However, it is important to understand that not all stocks are the same.
There are lots of stocks you could be buying that offer long-term results. However, there will also be times when you end up buying caveat emptor stocks that either have a probability of not offering results at all or offering ROI that does not make buying the stocks worthwhile.
At the end of the day, it is important to choose your stocks wisely to ensure you are not holding onto regrets but instead planning your next strategy to get the best from your time trading.
5 Things To Check Before You Buy A Stock
- Thoroughly research the market before deciding to invest:
Most stocks tend to move in accordance with the market. When the market is beaming, these stocks skyrocket. When the market plummets, these stocks fall. Researching the stock market exchange before investing is important to prevent buying volatile stocks.
Take the major index’s moving average into account to determine how frequently the market shifts. For instance, if you are planning to stay invested for three weeks, it is best to check the performance and average of the last 50 to 70 days to get an idea of how the market performed during that time and how frequently the stock’s value fluctuated.
Additionally, be sure to keep an eye out for major budget or earning announcements, as they tend to have an effect on how the market performs.
2. Identify and resonate with a sector:
When you have identified a sector that you are able to resonate with, it becomes easier to understand why the market is changing a certain way.
It will also prepare you to take precautionary steps on how you can protect yourself from the losses. Additionally, buying stocks from an industry that you are familiar with creates a sense of comfort.
In case you are unsure where to start, it is a great idea to check the Global Industry Classification Standard index for better understanding and clarity.
However, do not jump into an industry that is already running into losses. Instead, consider holding your interest till the industry recovers and then invest.
3. Conduct a self-audit for auditioning choices:
Once you have picked stocks from an industry that interests you, screen them for value, past performances, and ROI forecasts.
You will realize not all stocks within the same industry have been performing in the same pattern. Through this, you can identify and plan where you want to invest.
For instance, if you are looking for growth, find stocks that have higher projected growth rates. Whereas, if you are looking for value-driven and long-term investment stocks, then look for price-to-earnings ratios.
4. Consider investing in dividends:
If you are still struggling to decide if the stock market is for you, then investing in dividends is a practical idea. Interest in dividends gives similar assurance and value as a savings account.
These are issued by companies every quarter to their shareholders as rewards for their investment and trust in the company. Some companies even issue dividends in the form of stock shares.
Investing in dividends from sectors like oil and gas, banks, financial companies, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, raw materials, and utility items is worth investing in as they offer consistent results.
5. Keep an eye on charts:
Once you have decided on the stocks you are willing to invest in, consider checking their trend line to understand the nature of ROI you will be getting, the value they offer, and how they are making your portfolio better.
It is highly recommended to avoid buying stocks in a hurry or out of fear of missing out. Instead, consider taking a moment’s pause and asking yourself if the trade is an impulsive decision or if you have enough information to go forth with the investment.
Adding a logical reasoning behind your buying, selling, or holding decision ensures you are making the right choice.
Parting words
Stock markets are a great channel to multiply your revenue. However, it is crucial to pick your stocks carefully. Research, trend analysis, and keeping an eye out for current events can help you update your marketing strategy and get higher returns from every investment you are making.










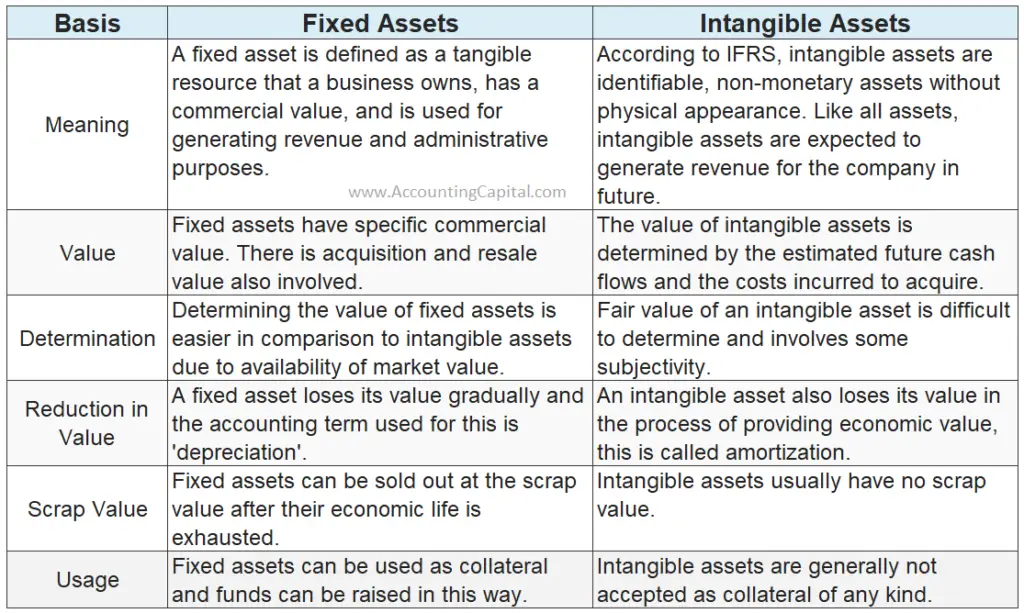
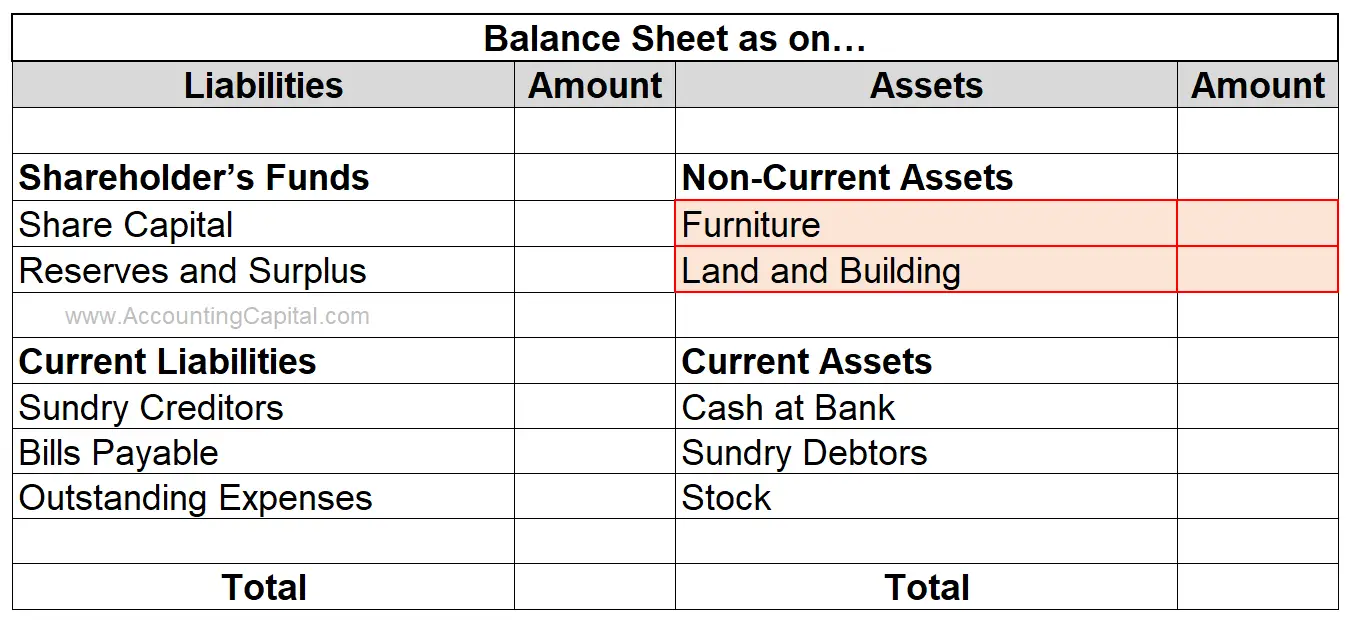 Related Topic –
Related Topic – 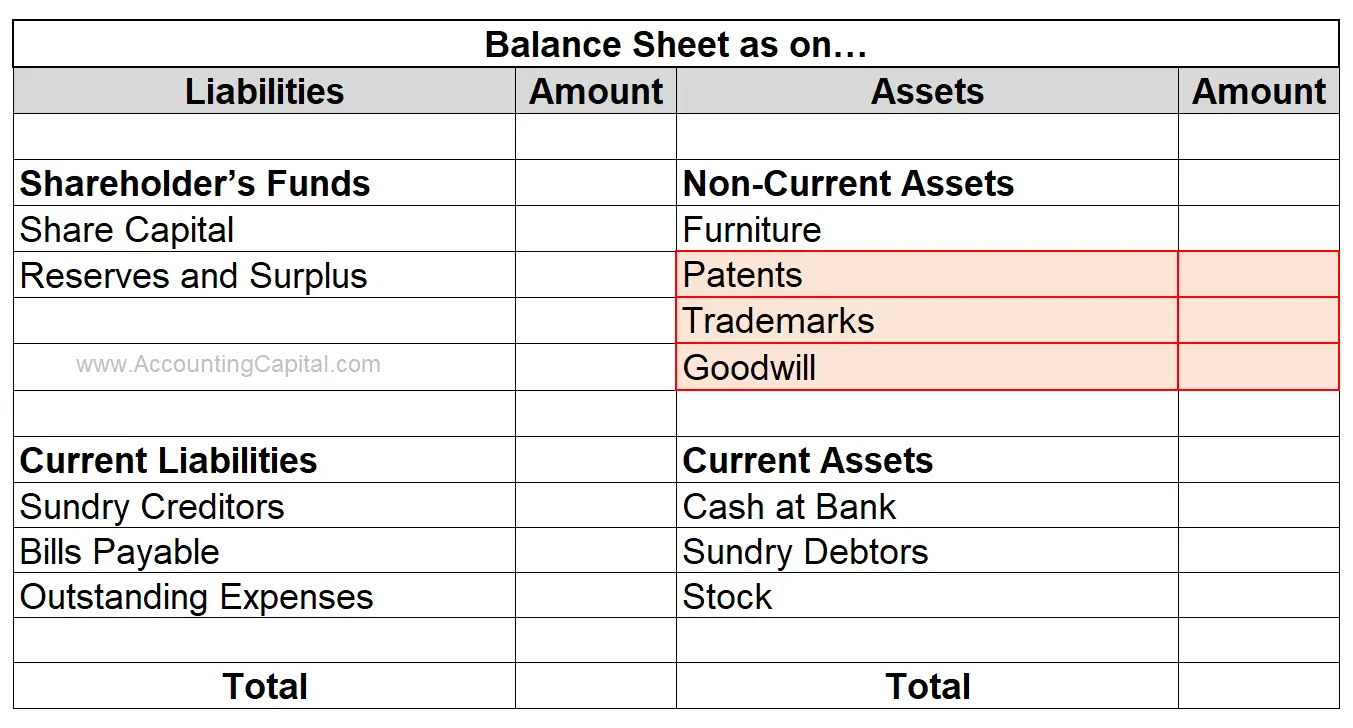



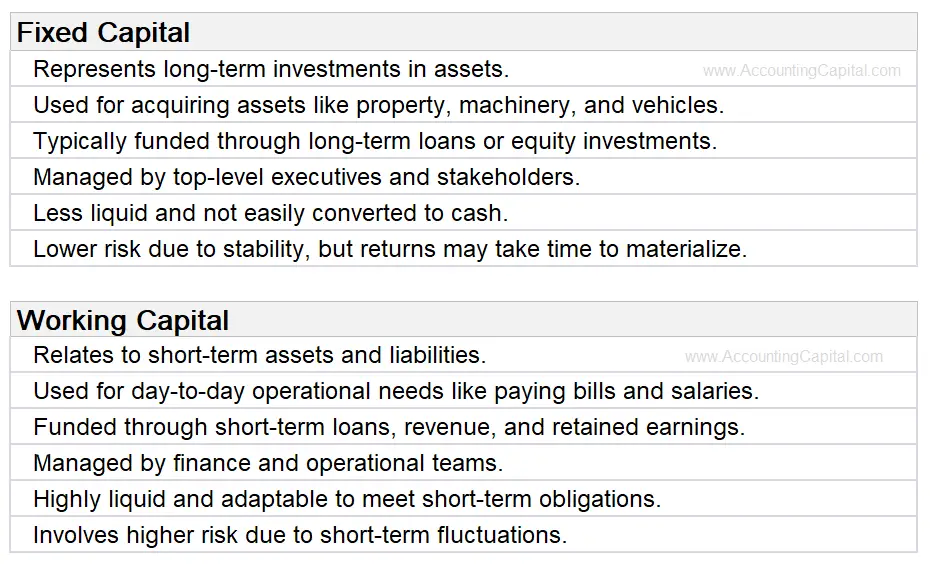 Both fixed and working capital are of equal importance for the existence and smooth functioning of the entity. Identifying the right source and amount of both fixed and working capital is a strategic task for an entity.
Both fixed and working capital are of equal importance for the existence and smooth functioning of the entity. Identifying the right source and amount of both fixed and working capital is a strategic task for an entity.